bean的什么周期
Spring Bean 的生命周期在整个 Spring 中占有很重要的位置,从BeanFactory或ApplicationContext取得的实例为Singleton,也就是预设为每一个Bean的别名只能维持一个实例,而不是每次都产生一个新的对象使用Singleton模式产生单一实例,在spring中,singleton属性默认是true,只有设定为false,则每次指定别名取得的Bean时都会产生一个新的实例,Spring只帮我们管理单例模式Bean的完整生命周期,对于prototype的bean,Spring在创建好交给使用者之后则不会再管理后续的生命周期。
过程
1.实例化一个Bean(一般通过反射创建)
2.按照Spring上下文对实例化的Bean进行配置(注入)
3.如果这个Bean已经实现了BeanNameAware接口,会调用它实现的setBeanName(String)方法,此处传递的就是Spring配置文件中Bean的id值
4.如果这个Bean已经实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,会调用它实现的setBeanFactory(setBeanFactory(BeanFactory)传递的是Spring工厂自身(可以用这个方式来获取其它Bean,只需在Spring配置文件中配置一个普通的Bean就可以)
5.如果这个Bean已经实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,会调用setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext)方法,传入Spring上下文(同样这个方式也可以实现步骤4的内容,但比4更好,因为ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,有更多的实现方法)
6.如果这个Bean关联了BeanPostProcessor接口,将会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object obj, String s)方法,BeanPostProcessor经常被用作是Bean内容的更改,并且由于这个是在Bean初始化结束时调用那个的方法,也可以被应用于内存或缓存技术
7.如果Bean在Spring配置文件中配置了init-method属性会自动调用其配置的初始化方法
8.如果这个Bean关联了BeanPostProcessor接口,将会调用postProcessAfterInitialization(Object obj, String s)方法
9.当Bean不再需要时,会经过清理阶段,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean这个接口,会调用那个其实现的destroy()方法
测试:
创建一个bean类
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class HelloWord implements
BeanNameAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware,
BeanPostProcessor,
DisposableBean{
public HelloWord(){
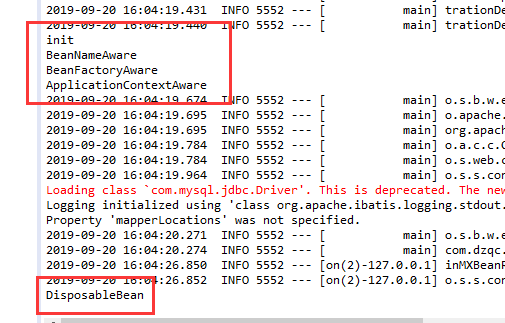
System.out.println("init");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanNameAware");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("ApplicationContextAware");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("DisposableBean");
}
}
配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TestController {
@Bean
public HelloWord getHelloWord() {
HelloWord h=new HelloWord();
return h;
}
}
输出: